What is Single Sign On?
Single Sign On (SSO) is an authentication process that allows a user to access multiple applications with one single set of login credentials. Users sign in once and gain access to all associated applications without the need to log in again for each one. This concept has been gaining traction in various sectors, from enterprise corporate environments to consumer applications, improving user experience and security. Learn more about single sign on https://www.wwpass.com/wwpass-sso to enhance your application’s security and usability.
The Importance of Single Sign On
The digital landscape today is vast and diverse, with users juggling numerous applications daily. The need for a robust authentication mechanism that simplifies this process is undeniable. Here are several reasons why SSO is critical:
- Simplified User Experience: SSO reduces the number of times a user has to log in, which can lead to fewer password-related frustrations.
- Increased Security: With fewer passwords to remember, the likelihood of password reuse or weak passwords decreases. SSO often comes with advanced authentication options, such as multi-factor authentication.
- Time Saving: IT staff do not have to spend as much time resetting passwords or handling authentication-related issues.
- Centralized User Management: Administrators can manage user permissions from a central interface, streamlining user onboarding and offboarding.
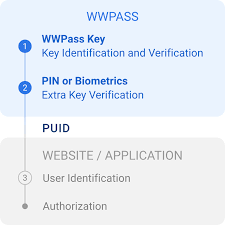
How Single Sign On Works

SSO works by establishing trust between a service provider and an identity provider. When a user attempts to access an application, the following process occurs:
- The user selects the application and clicks the login button.
- The application redirects the user to the identity provider for authentication.
- The user enters their credentials on a secure login page provided by the identity provider.
- If the credentials are valid, the identity provider generates an authentication token.
- This token is sent back to the application, which grants access based on the received token.
Common Protocols for Single Sign On
Several protocols are commonly used to implement SSO functionalities. Some of the most popular ones include:
- SAML (Security Assertion Markup Language): A widely used standard for exchanging authentication and authorization data between parties, particularly in enterprise settings.
- OAuth: Primarily used for token-based authentication and authorization, OAuth allows third-party services to exchange information without exposing user passwords.
- OpenID Connect: Built on top of OAuth 2.0, this protocol enables clients to verify the identity of an end-user based on the authentication performed by an authorization server.
Challenges and Considerations

While the benefits of SSO are numerous, it is essential to address some challenges that organizations may face during implementation:
- Single Point of Failure: If the SSO service goes down, users may lose access to all connected applications, which can disrupt business operations.
- Complexity of Migration: Transitioning from a traditional password-based system to SSO can be complex and requires careful planning and technical expertise.
- Security Risks: If an attacker gains access to a user’s SSO credentials, they may be granted access to all associated applications. Thus, robust security measures such as multi-factor authentication should be implemented.
Future of Single Sign On
As digital ecosystems continue to evolve, so too will the technologies surrounding SSO. Expect to see:
- Advanced Security Features: Technologies like biometric authentication and AI-driven security measures will increasingly be integrated into SSO systems.
- Greater Adoption in Consumer Applications: More applications, especially in mobile and web-based platforms, will incorporate SSO to streamline user experiences.
- Interoperability and Standards: As more organizations adopt SSO, there will be a push for interoperability between different SSO systems, promoting a seamless user experience across platforms.
Conclusion
Single Sign On represents a crucial advancement in user authentication methodologies that prioritizes user convenience and security. As businesses and consumers continue to seek more efficient and secure ways to access applications, SSO will play a vital role. Understanding its mechanics, benefits, and challenges will empower organizations to implement SSO strategies effectively, ensuring that they remain competitive and secure in the digital landscape.
